Now Reading: Sleep Science Shows Why Quality Matters More Than Duration
-
01
Sleep Science Shows Why Quality Matters More Than Duration
Sleep Science Shows Why Quality Matters More Than Duration

Discover the latest sleep science proving that how you sleep matters more than how long you sleep. Learn what defines sleep quality, how to improve it, and why it affects your health, focus, and longevity.
Why We’re Asking the Wrong Sleep Question
For years, we’ve been told that eight hours of sleep a night is the magic number for good health. But new research in sleep science is rewriting the rules: it’s not just about how long you sleep — it’s about how well you sleep.
From brain restoration to hormone balance and emotional stability, the quality of your sleep plays a far bigger role than the clock on your nightstand. In this article, we’ll explore what sleep quality really means, why it matters more than duration, and how you can improve it starting tonight.
The Science of Sleep: What Happens When You Close Your Eyes
Sleep isn’t a uniform state — it’s a complex biological process that unfolds in cycles. Each cycle includes several stages, and your health depends on spending enough time in each.
The Four Stages of Sleep:
- Stage 1 (Light Sleep): The transition from wakefulness; lasts a few minutes.
- Stage 2: Heart rate slows, body temperature drops, and the brain begins processing memories.
- Stage 3 (Deep Sleep): The body repairs muscles, boosts immunity, and releases growth hormones.
- Stage 4 (REM Sleep): The mind consolidates learning and emotional experiences.
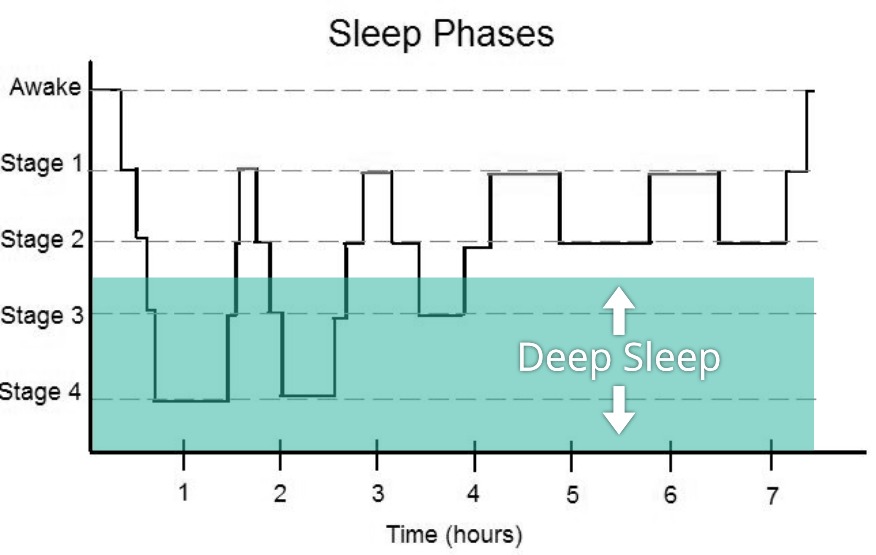
Each night, you move through 4–6 of these cycles. Missing or shortening certain stages — especially deep or REM sleep — reduces the overall quality of rest, even if you hit the 8-hour mark.
Sleep Duration vs. Sleep Quality: The Crucial Difference
Most adults focus on quantity — “Did I get enough sleep?” — instead of quality, which is the better question: “Did I get enough restorative sleep?”
Key Differences:
| Aspect | Sleep Duration | Sleep Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total time spent asleep | Time spent in restorative stages (deep & REM) |
| Focus | Quantity (hours) | Efficiency, continuity, depth |
| Impact | Basic recovery | Cognitive, emotional, and physical optimization |
| Measured by | Hours on the clock | Sleep efficiency % and sleep stage balance |
In short, 8 hours of fragmented, shallow sleep can leave you more tired than 6 hours of high-quality, uninterrupted rest.
Why Sleep Quality Matters More
Sleep quality determines how effectively your body and brain recover. When sleep is deep and consistent, it triggers crucial biological functions that duration alone can’t achieve.
1. Memory & Learning
During REM sleep, your brain consolidates memories and processes new information. Poor-quality sleep disrupts this, leading to forgetfulness and slower learning.
2. Hormone Regulation
Deep sleep helps regulate cortisol (stress) and insulin (blood sugar). Low-quality sleep throws these hormones off balance, increasing the risk of weight gain, mood swings, and diabetes.
3. Cellular Repair
Deep stages of sleep trigger growth hormones that repair tissue and strengthen immunity — essential for recovery from stress, exercise, or illness.
4. Emotional Health
Sleep quality directly influences mental resilience. Studies show that disrupted sleepers are 60% more reactive to negative emotions and have a higher risk of anxiety or depression.
What the Latest Sleep Research Reveals
Recent studies from institutions like Harvard Medical School and the National Sleep Foundation confirm that sleep efficiency — not just duration — predicts overall health outcomes.
- Harvard Study (2023): Found that individuals with 85%+ sleep efficiency had better cognitive performance regardless of total hours slept.
- Sleep Medicine Review (2024): Identified that fragmented sleep increases inflammatory markers, even when total duration is sufficient.
- Stanford Neuroscience Lab: Showed that deep sleep quality improves memory recall by up to 40%, independent of duration.
The takeaway? You can’t make up for poor sleep quality by sleeping longer.
How to Measure Your Sleep Quality
You don’t need a lab to track your sleep. Thanks to technology, wearable sleep trackers and smartphone apps can give you actionable insights.
Key Metrics to Watch:
- Sleep Efficiency: % of time spent asleep vs. time in bed (aim for 85–90%).
- Sleep Latency: Time it takes to fall asleep (under 20 minutes is healthy).
- REM and Deep Sleep: Combined, they should make up around 40–50% of your total sleep.
- Awakenings: Fewer interruptions = better recovery.
Popular tools include the Oura Ring, Fitbit, Apple Watch, and apps like Sleep Cycle or Pillow.
Practical Ways to Improve Sleep Quality
Improving sleep quality often means small, consistent lifestyle changes — not expensive products or extreme hacks.
1. Keep a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily, even on weekends. This strengthens your circadian rhythm, the internal clock that regulates rest.
2. Optimize Your Environment
- Keep your room cool (18–20°C).
- Block light using blackout curtains or an eye mask.
- Eliminate noise or use white noise machines.
3. Limit Screen Time Before Bed
Blue light from devices suppresses melatonin. Power down screens at least 60 minutes before bedtime or use blue-light filters.
4. Watch What You Eat and Drink
Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Try magnesium-rich foods like bananas or almonds for better relaxation.
5. Incorporate Relaxation Techniques
Meditation, breathing exercises, or reading a physical book can help signal your body that it’s time to unwind.
6. Exercise Regularly
Moderate physical activity, especially earlier in the day, improves deep sleep — but avoid intense workouts right before bed.
The Role of Technology and Sleep Tech
The global sleep tech industry is booming, with innovations aimed at improving sleep quality through data and smart environments.
- Smart Mattresses: Adjust firmness or temperature automatically.
- AI-Powered Sleep Apps: Use sound analysis and heart rate monitoring to detect disruptions.
- Smart Lights: Gradually dim and simulate natural sunrise patterns for better wake-up transitions.
Sleep optimization is becoming the next frontier of personalized health tech, where your bed could become your most powerful wellness device.
Common Myths About Sleep
Let’s bust a few persistent misconceptions:
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| “I can catch up on weekends.” | Sleep debt can’t be fully recovered. Quality matters daily. |
| “Older adults need less sleep.” | They often sleep less due to changes in rhythm, not need. |
| “Alcohol helps you sleep.” | It may make you drowsy, but it disrupts REM and causes poor quality rest. |
| “Napping ruins night sleep.” | Short naps (20–30 mins) can boost alertness without interference. |
The Future of Sleep Science
Researchers are now exploring genetic differences in sleep needs and developing AI-driven sleep therapies tailored to individuals. From smart bedding that detects stress to neurostimulators that enhance deep sleep, the next decade will redefine how we rest.
Sleep will no longer be seen as “time off” — but as a biological investment in productivity, mood, and longevity.
Final Thoughts: Sleep Smart, Not Just Long
In today’s hustle culture, sleep often feels like a luxury. But science reminds us it’s the foundation of everything — health, focus, creativity, and emotional stability.
So instead of counting hours, start counting quality. Build habits that protect your rest, and you’ll not only sleep better — you’ll live better.



















